Structural Steel is formed with a specific shape and it is used in any kind of steel construction. These materials are of definite quality of chemical composition and proper strength. Some of the structural steels are hot rolled products such as the Black Iron Sheet, Angle Bar, Channel Bar and Beams.
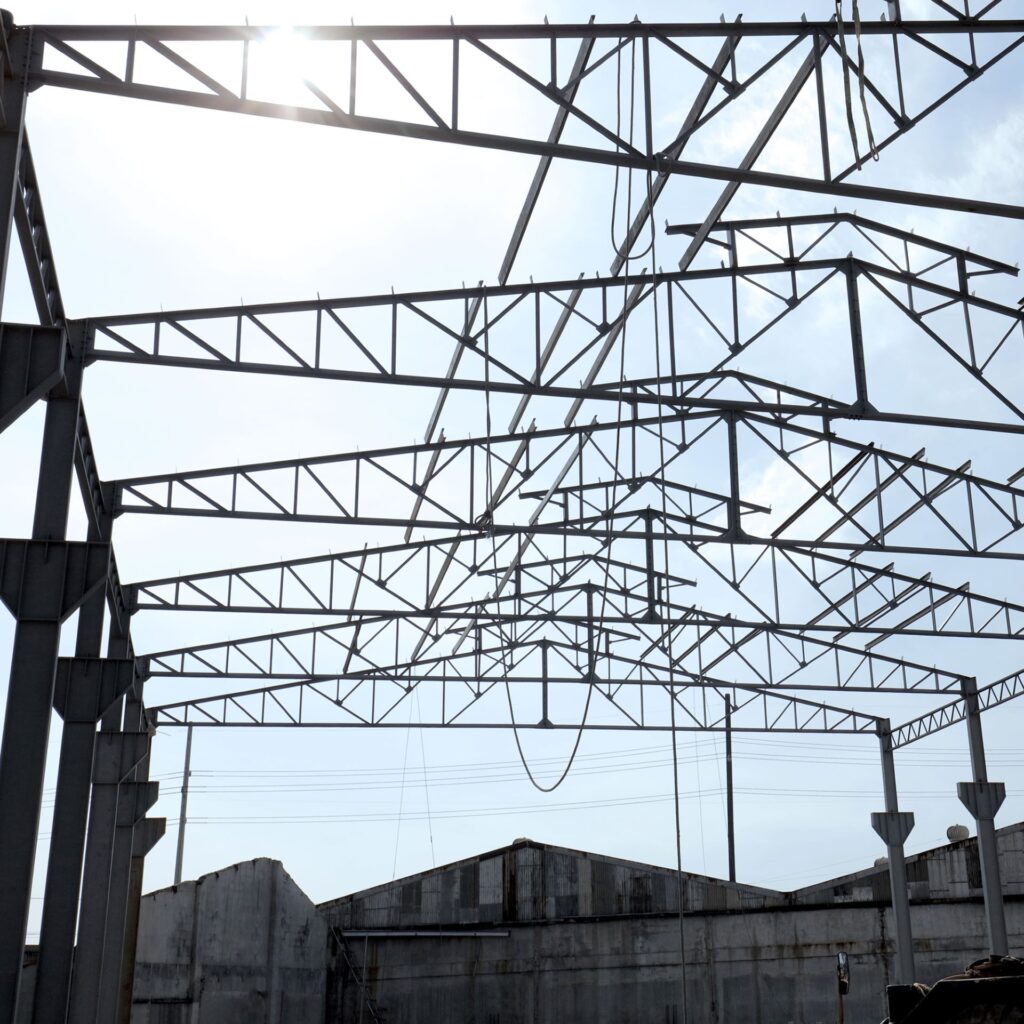

A structural steel shape is a profile formed with a detailed cross section. Below are some of the common structural steel shapes.
| Steel | Shape |
|---|---|
| I-beam | An I-shaped cross section with flanges on both side |
| Z-Bar | Half a flange going in opposite directions |
| Angle Bar | An L-shaped cross section |
| T-Bar | T-shaped cross section |
| Rectangular Bar | A rectangular, cross sectioned long piece of steel |
| Rod | A round or square long piece of steel |
There are different structures which come in the edges of steel structures. These structures may be utilized for the industrial, residential, office and commercial uses. The design for the bridge is for roadways and railway lines. While the structures like towers are utilized for various purposes like power transmission, nodal towers for mobile network, radar, telephone relay towers, and many more.
Design and construction of steel structures are determined by its properties. These properties are the tensile strength, hardness, notch toughness, and fatigue stress which are essential to know before determining which type of structural steel will suit in the construction of structural buildings.
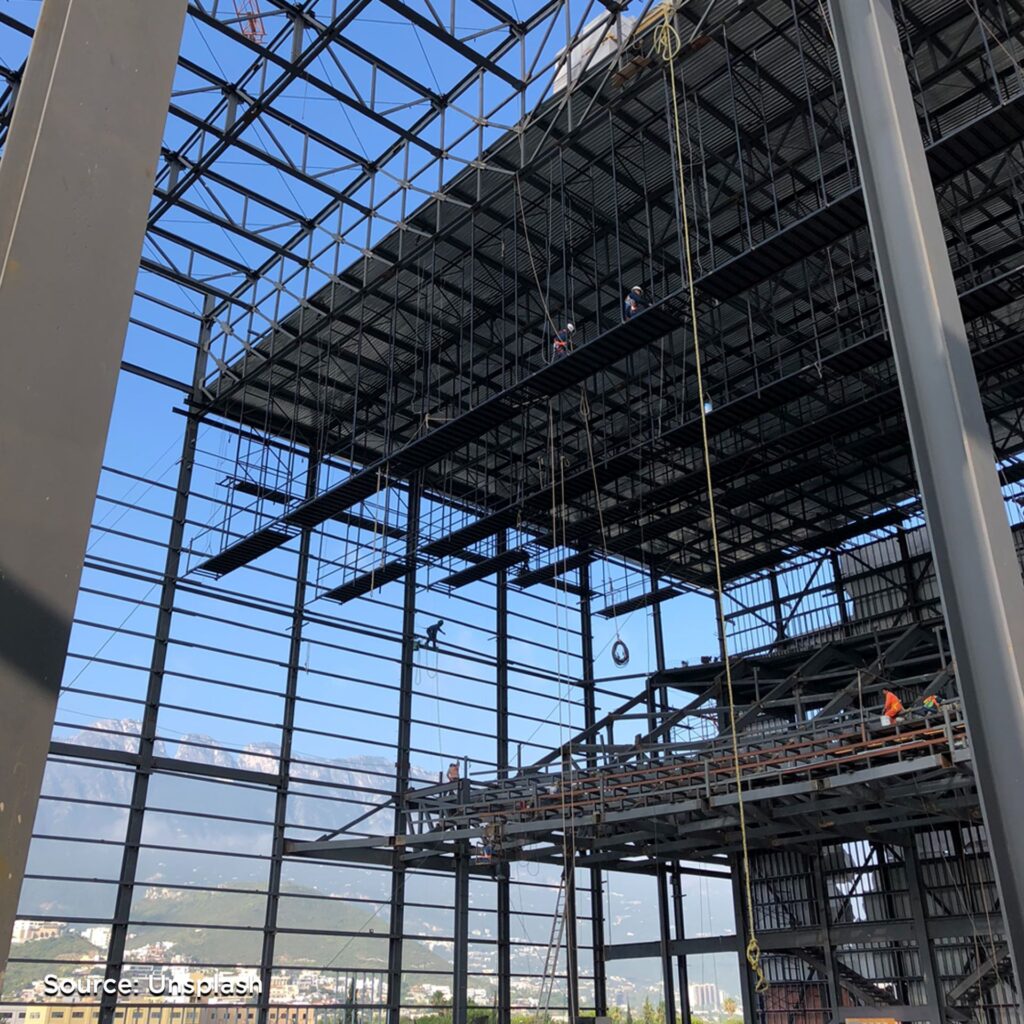

Tensile Strength
Tensile strength of steel is determined by the limit up to which steel can be stretched without breaking. Structural steel has high tensile strength and is preferred over other materials for construction. The stress-strain curve for the steel is normally acquired by showing tensile tests on any standard steel sample. Tensile strength of the steel can be determined in terms of yield and ultimate strength.
Hardness
Hardness is the capacity of steel structure to tolerate inelastic deformation. Inelastic deformation is when steel is stressed beyond its elastic limit. The hardness also defines the several properties of specific steel, like resistance to wear, toughness, and formability. There are three different standard tests to evaluate steel hardness, these are the Brinell Test, the Rockwell Test, Knoop Hardness Test and the Bicker Hardness Test.
Notch Toughness
There is a chance of microscopic cracks in a material or the material may develop such cracks as an effect of some cycles of loading. These cracks may cause structural collapse which is very dangerous. Thus, to guarantee that this should not happen, materials in which the cracks develop slowly are preferred. These kinds of steel are identified as notch-tough steels and the sum of energy it holds is measured by impacting the notch sample.
Fatigue strength
A part of the structure, which is planned to transmit a single monotonically static load, may fail if the similar load is pertained regularly a large number of times. For example, a thin rod is assessed, it bent back and forth past yielding fails after a few cycles of frequent bending. This type of failure is called fatigue.
Are you looking for a trusted steel supplier that provides good quality steel products at competitive prices? Contact TKL Steel Corporation, the trusted steel supplier in the industry with over 35 years of experience in valuing the trust of our customers and providing good quality steel products at competitive prices. For inquiries, you may reach us at 0917 808 8528, 0939 909 0146, (02) 8588 1155, email us at sales@tkl.com.ph or send us a message on our official Facebook page www.facebook.com/tklsteelph and our friendly sales associate will assist you with your steel requirements.
Sources:
Steel Structures. (n.d.). Retrieved October 03, 2020, from https://civilengineeringbible.com/subtopics.php?i=97